About this myth
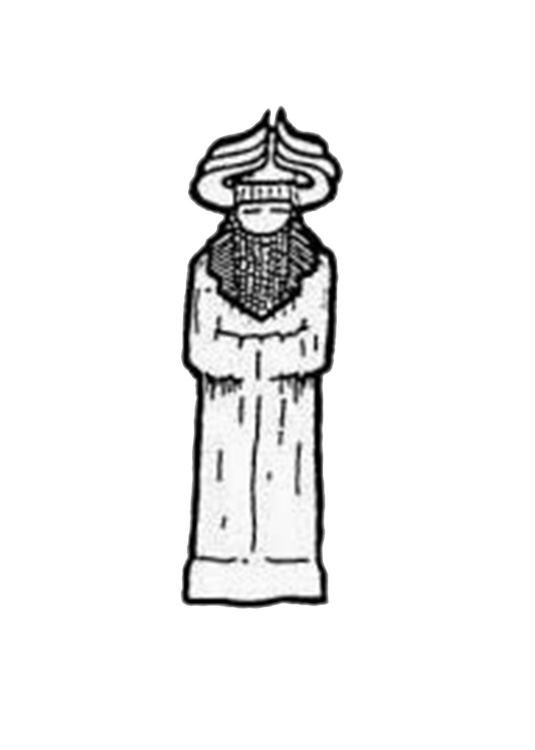
Adapa and the South Wind is a Creation myth originating from the Sumerian belief system. The main deity depicted in this myth is likely Adapa. Others include An, and Dumuzi.
In a nutshell
Myth summary
Sit tight. More information about this is coming soon.
Attested: Unknown
Created: Unknown
Main deity: Adapa
Belief system: Sumerian
Origin: Asia › Middle Africa › Iraq
Belief system
Sumerian Religion
Polytheistic
Sumerian religion refers to spiritual beliefs practiced from ca. 4500-1900 BCE in Mesopotamia, or modern-day southern Iraq. Many deities were diffused into other Mesopotamian cultures.
arrow_forward More info Adapa
Main deity
Adapa was a figure from Eridu that came to be known as the "wise man" after Enki provided him such wisdom.
arrow_forward More info Texts related to this myth
See full texts of this myth via related artifacts. Where available, a translation is included.
All texts
| Title | - notes
- translate
- vertical_split
- format_list_numbered
- assignment_turned_in
|